Measurement
Metric system
The metric system is a way of measuring things, like length, weight, and volume, using units that are based on the number 10. It’s used by most countries around the world because it’s simple and easy to use.
Here’s how the metric system works for some of the basic measurements:
1. Length (How long something is)
The basic unit of length in the metric system is the meter (m). Here are the most common metric units for length:
– Millimeter (mm): Smallest unit, like the thickness of a coin.
– Centimeter (cm): 1 centimeter = 10 millimeters. A pencil is about 10 cm long.
– Meter (m): 1 meter = 100 centimeters. A door is about 2 meters tall.
– Kilometer (km): 1 kilometer = 1,000 meters. You measure the distance between towns in kilometers.
2. Weight (How heavy something is)
The basic unit of weight in the metric system is the gram (g).
– Milligram (mg): Very light things, like medicine, are measured in milligrams.
– Gram (g): 1 gram = 1,000 milligrams. A paper clip weighs about 1 gram.
– Kilogram (kg): 1 kilogram = 1,000 grams. A bag of rice might weigh 1 kilogram.
3. Volume (How much space something takes up)
The basic unit of volume in the metric system is the liter (L).
– Milliliter (mL): A few drops of water are measured in milliliters.
– Liter (L): 1 liter = 1,000 milliliters. A bottle of soda is about 1 liter.
Place value chart of metric measures
What is the Metric System?
The metric system is used to measure things like:
– Length (How long something is)
– Mass (How heavy something is)
– Volume (How much space something takes up)
Each type of measurement has different units:
– Length: millimeters (mm), centimeters (cm), meters (m), kilometers (km)
– Mass: milligrams (mg), grams (g), kilograms (kg)
– Volume: milliliters (mL), liters (L)
Place Value Chart for Metric Units:
The place value chart looks like this:
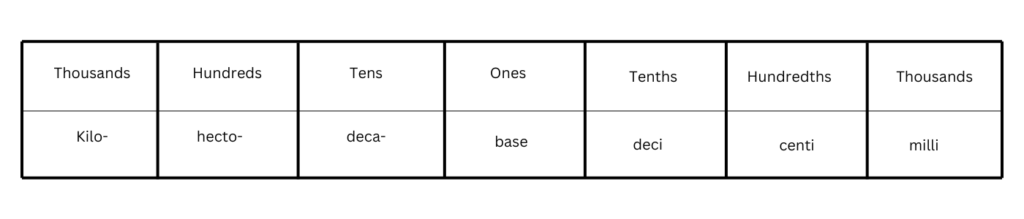
1. The base unit (in the center of the chart) is the main unit:
– Meter (m) for length
– Gram (g) for mass
– Liter (L) for volume
2. Moving Left on the chart means bigger units (each step is 10 times bigger):
– Deca- means 10 times the base unit.
– Hecto- means 100 times the base unit.
– Kilo- means 1,000 times the base unit.
3. Moving Right on the chart means smaller units (each step is 10 times smaller):
– Deci- means 1/10 of the base unit.
– Centi- means 1/100 of the base unit.
– Milli- means 1/1,000 of the base unit.
Example of Metric Length:
Let’s say you want to know how many meters are in a kilometer:
– Kilo means 1,000, so 1 kilometer = 1,000 meters.
Now let’s say you want to know how many centimeters are in a meter:
– Centi means 1/100, so 1 meter = 100 centimeters.
How to Use the Place Value Chart for Conversions:
– To convert from a larger unit to a smaller unit (like kilometers to meters), multiply by 10 for each step to the right.
– To convert from a smaller unit to a larger unit (like centimeters to meters), divide by 10 for each step to the left.
Conversion of metric measures
Metric Units to Remember:
– Length: millimeters (mm), centimeters (cm), meters (m), kilometers (km)
– Mass (Weight): milligrams (mg), grams (g), kilograms (kg)
– Volume (Capacity): milliliters (mL), liters (L)
How to Convert Metric Units
In the metric system, we convert between units by moving up or down the place value chart, which is based on powers of 10. Each step to the left is 10 times bigger, and each step to the right is 10 times smaller.
Key Conversion Facts:
– 1 kilometer (km) = 1,000 meters (m)
– 1 meter (m) = 100 centimeters (cm)
– 1 centimeter (cm) = 10 millimeters (mm)
– 1 kilogram (kg) = 1,000 grams (g)
– 1 gram (g) = 1,000 milligrams (mg)
– 1 liter (L) = 1,000 milliliters (mL)
### Conversion Steps
#### 1. From Larger Unit to Smaller Unit (Multiply by 10, 100, or 1,000):
– When converting from a larger unit to a smaller unit (e.g., meters to centimeters), multiply.
– Example: To convert 5 meters to centimeters:
– 1 meter = 100 centimeters, so 5 meters = 5 × 100 = 500 centimeters.
2. From Smaller Unit to Larger Unit (Divide by 10, 100, or 1,000):
– When converting from a smaller unit to a larger unit (e.g., centimeters to meters), divide.
– Example: To convert 250 centimeters to meters:
– 100 centimeters = 1 meter, so 250 ÷ 100 = 2.5 meters.
Conversion Examples
Length:
1. Convert 3 kilometers to meters:
– 1 kilometer = 1,000 meters.
– 3 kilometers = 3 × 1,000 = 3,000 meters.
2. Convert 200 centimeters to meters:
– 1 meter = 100 centimeters.
– 200 ÷ 100 = 2 meters.
Mass (Weight):
1. Convert 4 kilograms to grams:
– 1 kilogram = 1,000 grams.
– 4 × 1,000 = 4,000 grams.
2. Convert 3,500 grams to kilograms:
– 1 kilogram = 1,000 grams.
– 3,500 ÷ 1,000 = 3.5 kilograms.
Volume (Capacity):
1. Convert 5 liters to milliliters:
– 1 liter = 1,000 milliliters.
– 5 × 1,000 = 5,000 milliliters.
2. Convert 3,000 milliliters to liters:
– 1 liter = 1,000 milliliters.
– 3,000 ÷ 1,000 = 3 liters.
Addition and subtraction of metric measures
Important Steps for Addition and Subtraction of Metric Measures
1. Align the Units: Always make sure the units are the same before adding or subtracting. For example, only add meters to meters, grams to grams, etc.
2. Convert Units if Necessary: If the measurements are in different units, convert them to the same unit first.
3. Add or Subtract: Once the units are aligned, add or subtract as usual.
4. Convert Back if Needed: If required, convert your answer back to a different unit.
Example 1: Addition of Metric Measures
Problem:
Add 3 meters 25 centimeters and 1 meter 75 centimeters.
Steps:
1. Align the units by converting everything to the same unit (in this case, centimeters).
– 3 meters = 300 centimeters
– So, 3 meters 25 centimeters = 325 centimeters.
– 1 meter 75 centimeters = 175 centimeters.
2. Add the measurements:
325 cm + 175 cm = 500 cm
3. Convert back if needed:
– 500 cm = 5 meters.
Answer: 3 meters 25 centimeters + 1 meter 75 centimeters = 5 meters.
Example 2: Subtraction of Metric Measures
Problem:
Subtract 2 liters 500 milliliters from 5 liters.
Steps:
1. Convert everything to the same unit (in this case, milliliters).
– 5 liters = 5,000 milliliters
– So, 5 liters = 5,000 milliliters.
– 2 liters 500 milliliters = 2,500 milliliters.
2. Subtract the measurements:
5,000 mL – 2,500 mL = 2,500 mL
3. Convert back if needed:
– 2,500 mL = 2 liters 500 milliliters.
Answer: 5 liters – 2 liters 500 milliliters = 2 liters 500 milliliters.
