Multiplication upto 50
What is Multiplication?
Multiplication is like adding groups of the same size. For example, if you have 4 groups of 3 apples each, you can add the apples together:
3+3+3+3=12
Or, you can multiply:
4×3=12
Here, 4 is the number of groups, and 3 is the number of apples in each group.
Grouping
What is Grouping?
Grouping means putting things together in sets or groups that have the same number of items. For example, if you have 10 apples, you can group them into sets of 2.
Example of Grouping
Let’s say you have 12 candies. You want to put them into groups of 3. Here’s how you can do it:
Count out 3 candies and put them in a group.
Repeat until you have no more candies left.
So, you would have:
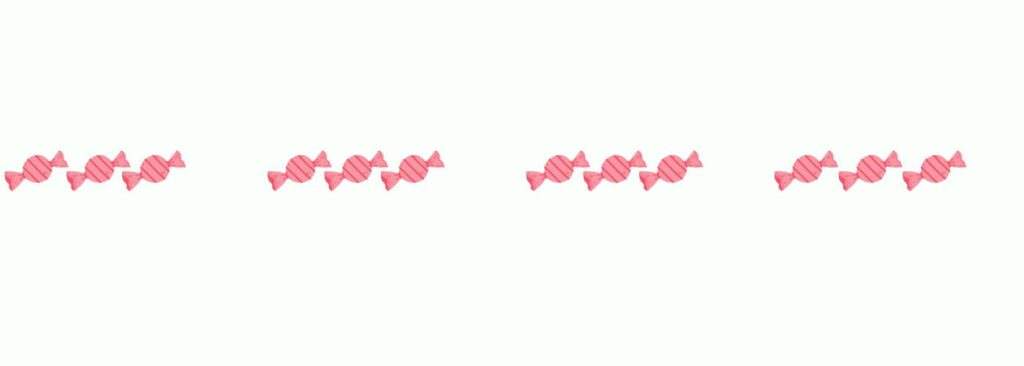
Now, you have 4 groups of 3 candies each.
Vertical multiplication
Vertical multiplication is a method where you write the numbers to be multiplied in a column format, with one number directly under the other. You then multiply each digit step by step, starting from the rightmost digit.
Steps for Vertical Multiplication
Let’s learn the steps with an example.
Example: Multiply 23 by 4
Write the numbers vertically:
23 x 4 _____
Multiply the digit in the ones place of the bottom number (4) by the digit in the ones place of the top number (3):
4×3=12
Write 2 in the ones place below the line and carry over 1 to the next column:
Multiply 2 digit number
Here’s an example:
Example: 12 × 3
Step-by-Step Explanation
1. Write the problem vertically:
– Write 12 on top and 3 below it.
“`
12
× 3
—-
“`
2. Multiply the digit in the ones place of the bottom number by the digit in the ones place of the top number:
– Multiply 3 (bottom) by 2 (top ones place).
– 3 × 2 = 6.
– Write the 6 below the line in the ones place.
“`
12
× 3
—-
6 (Write the 6 under the ones column)
“`
3. Multiply the digit in the ones place of the bottom number by the digit in the tens place of the top number:
– Multiply 3 (bottom) by 1 (top tens place).
– 3 × 1 = 3.
– Write the 3 next to the 6.
“`
12
× 3
—-
36 (Write the 3 under the tens column)
“`
Visual Aid Example
Let’s draw this out step-by-step:
1. Start with the setup:
“`
12
× 3
—-
“`
2. Multiply the ones place (2 × 3):
“`
12
× 3
—-
6
“`
3. Multiply the tens place (1 × 3):
“`
12
× 3
—-
36
“`
Conclusion
To summarize:
– You multiply the bottom number by each digit of the top number starting from the right (ones place).
– Write each result directly below the corresponding place value column.
– Combine the results to get the final answer.
Regrouping
Explaining regrouping in multiplication involves introducing them to the concept of carrying over numbers, similar to how they might already do in addition. Let’s go through a step-by-step example to make it easy to understand.
Example: 14 × 3
Step-by-Step Explanation
1. Write the problem vertically:
– Write 14 on top and 3 below it.
“`
14
× 3
—-
“`
2. Multiply the digit in the ones place of the bottom number by the digit in the ones place of the top number**:
– Multiply 3 (bottom) by 4 (top ones place).
– 3 × 4 = 12.
– Write the 2 in the ones place below the line and carry over the 1 to the next column.
“`
14
× 3
—-
2 (Write 2 in the ones column and carry over 1)
“`
3. Multiply the digit in the ones place of the bottom number by the digit in the tens place of the top number, then add the carried over number**:
– Multiply 3 (bottom) by 1 (top tens place).
– 3 × 1 = 3.
– Add the carried over 1.
– 3 + 1 = 4.
– Write the 4 in the tens place next to the 2.
“`
14
× 3
—-
42 (Write 4 in the tens column)
“`
Visual Aid Example
Let’s draw this out step-by-step:
1. Start with the setup:
“`
14
× 3
—-
“`
2. Multiply the ones place (4 × 3) and carry over if needed:
“`
14
× 3
—-
2 (3 × 4 = 12, write 2 and carry over 1)
“`
3. Multiply the tens place (1 × 3), add the carried over number, and write the result:
“`
14
× 3
—-
42 (3 × 1 = 3, plus the carried over 1 equals 4)
“`
Conclusion
To summarize:
– Multiply the bottom number by the ones place of the top number and write the result below. If the result is 10 or more, write the ones digit and carry over the tens digit.
– Multiply the bottom number by the tens place of the top number, add any carried over number, and write the result.
– Combine the results to get the final answer.
In this example, 14 × 3 = 42. This method shows how to handle larger products by carrying over, which is an essential part of understanding multiplication.
Word problem
Word Problem Example:
Lily has 3 baskets. Each basket has 5 apples. How many apples does Lily have in total?
Step-by-Step Explanation
1. Identify the numbers and what they represent:
– 3 baskets (the number of groups)
– 5 apples in each basket (the number of items in each group)
2.Set up the multiplication problem:
– Explain that to find the total number of apples, we need to multiply the number of baskets by the number of apples in each basket.
– Write the multiplication equation: 3 × 5.
3. Solve the multiplication problem:
– Multiply 3 (baskets) by 5 (apples per basket).
– Use a visual aid like drawing baskets and apples or using counters.
“`
3 × 5 = 15
“`
4. **Explain the answer:
– Lily has 15 apples in total.
– Write the final answer clearly: 3 × 5 = 15.
Visual Aid Example
You can use drawings to help visualize the problem:
1. Draw 3 baskets:
“`
Basket 1:
Basket 2:
Basket 3:
“`
2. Count all the apples together:
– Count: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 (Basket 1)
– Count: 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 (Basket 2)
– Count: 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 (Basket 3)
3. Explain that the total number of apples is 15.
To summarize:
– Read the word problem and understand the context.
– Identify the numbers and their meanings.
– Set up and solve the multiplication equation.
– Use visual aids to help understand and verify the solution.
– Write and explain the final answer.

